March 19, 2014
NASA Spacecraft Reveal New “Zebra Stripes” Structure in Earth’s Inner Radiation Belt
Scientists have discovered a new, persistent structure in Earth’s inner radiation belt using data from the twin NASA Van Allen Probes spacecraft. Most surprisingly, this structure is produced by the slow rotation of Earth, previously considered incapable of affecting the motion of radiation belt particles, which have velocities approaching the speed of light.
Data from the Radiation Belt Storm Probes Ion Composition Experiment (RBSPICE) on board each of the twin spacecraft orbiting Earth revealed that the highly energized population of electrons of the inner radiation belt is organized into very structured patterns that resemble slanted zebra stripes. Scientists had previously believed that increased solar wind activity was the primary force behind any structures in our planet’s radiation belts. These zebra stripes were shown to be visible even during low solar wind activity, which prompted a search for a new physical mechanism of their generation. That quest led to the surprising discovery that the stripes are caused by rotation of Earth. The findings are reported in the Mar. 20 issue of the journal Nature.
The Radiation Belt Storm Probes Ion Composition Experiment (RBSPICE) is a time-of-flight versus energy spectrometer, the most prominent feature of which is the sensor known as the “puck” (because of its resemblance to a hockey puck). RBSPICE measures medium energy protons, electrons, and ions (H+, He+, and O+) as functions of energy and angle, and is capable of measuring the full range of expected ring current energies, intensities, and ion compositions from quiet conditions to extreme events, with a factor of ten margin against intensity saturation.
Credit: NASA/JHUAPL
“It is because of the unprecedented high energy and temporal resolution of our energetic particle experiment, RBSPICE, that we now understand that the inner belt electrons are, in fact, always organized in zebra patterns,” said Aleksandr Ukhorskiy of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Md., co-investigator on RBSPICE and lead author of the paper. “Furthermore, our modeling clearly identifies Earth’s rotation as the mechanism creating these patterns. It is truly humbling, as a theoretician, to see how quickly new data can change our understanding of physical properties.”
Because of the tilt in Earth’s magnetic field axis, the planet’s rotation generates an oscillating, weak electric field that permeates through the entire inner radiation belt. To understand how that field affects the electrons, Ukhorskiy suggested an analogy: “If the inner belt electron populations are viewed as a viscous fluid, these global oscillations slowly stretch and fold that fluid, much like taffy is stretched and folded in a candy store machine,” he said. This stretching and folding process results in the striped pattern observed across the entire inner electron belt, extending from above Earth’s atmosphere (about 500 miles, or 800 kilometers, above the planet’s surface) up to roughly 8,000 miles (13,000 kilometers).
The radiation belts are dynamic doughnut-shaped regions around our planet, extending high above the atmosphere, made up of high-energy particles (electrons and ions) that are trapped by Earth’s magnetic field. Radiation levels across the belts are affected by solar activity (such as solar storms) and can ebb and flow. During active conditions, radiation levels can dramatically increase, which can create hazardous space weather conditions that harm orbiting spacecraft and endanger humans in space. It is the goal of the Van Allen Probes mission to understand how and why radiation levels in the belts change with time.
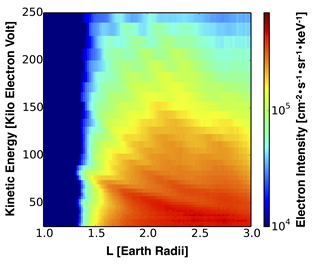
"Zebra stripes" in the inner radiation belt: An example of energetic electron spectra, measured on June 18, 2013 by NASA's twin Van Allen Probes in the inner radiation belt during quiet time during low solar activity. The striped, banded pattern is caused by the rotation of the Earth, previously thought to have no effect on the highly energetic particles of the radiation belt.
Credit: A. Ukhorskiy/JHUAPL
“This is another fundamental understanding made possible thanks to the highly detailed data being returned from these remarkable spacecraft,” said Louis Lanzerotti, distinguished research professor of physics at the Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research at the New Jersey Institute of Technology, principal investigator for RBSPICE, and a co-author on the paper. “It is amazing how Earth’s space environment, including the radiation belts, continue to surprise us even after we have studied them for over 50 years. Our understanding of the complex structures of the belts, and the processes behind the belts’ behaviors, continues to grow, all of which contribute to the eventual goal of providing accurate space weather modeling.”
“This finding tells us something new and important about how the universe operates,” said Barry Mauk of APL, Van Allen Probes project scientist and an author of the paper. “The new results reveal a new large-scale physical mechanism that can be important for planetary radiation belts throughout the solar system. An instrument similar to RBSPICE is now on its way to Jupiter on NASA’s Juno mission, and we will be looking for the existence of zebra stripe-like patterns in Jupiter’s radiation belts.”
NASA launched the twin Van Allen probes in the summer of 2012. APL built and operates the probes for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. The Van Allen Probes are the second mission in NASA’s Living With a Star program, managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. The program explores aspects of the connected sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society.
This animation uses actual data gathered by the Van Allen Probes from within Earth’s radiation belts, showing the formation of a zebra stripe pattern. It is caused by a process that can be likened to the stretching and folding of a taffy-like fluid; in this case, the clouds of electrons that make up the radiation belts. The stretching and folding occurs as a result of Earth’s rotation with its tilted magnetic axis.
Credit: A. Ukhorskiy/JHUAPL
Media contacts:
Geoff Brown, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, 240-228-5618, geoffrey.brown@jhuapl.edu
Robert Florida, New Jersey Institute of Technology, 201-725-6435, robert.florida@njit.edu
The Applied Physics Laboratory, a not-for-profit division of The Johns Hopkins University, meets critical national challenges through the innovative application of science and technology. For more information, visit www.jhuapl.edu.

